All SI Units Table in Chemistry (With Symbols & Quantities)
Whether you’re studying for an upcoming chemistry quiz or exploring scientific measurement systems, SI Units (International System of Units) is crucial for them. These units create a universal language of science — used in chemistry labs and scientific research across the globe.
This guide gives you a complete table of SI units used in chemistry, along with definitions and practical examples.
What Are SI Units in Chemistry?
SI Units, or the Système International d’Unités, are the globally accepted standard for measuring physical quantities. In chemistry, they help express things like mass, temperature, amount of substance, and concentration accurately and consistently.
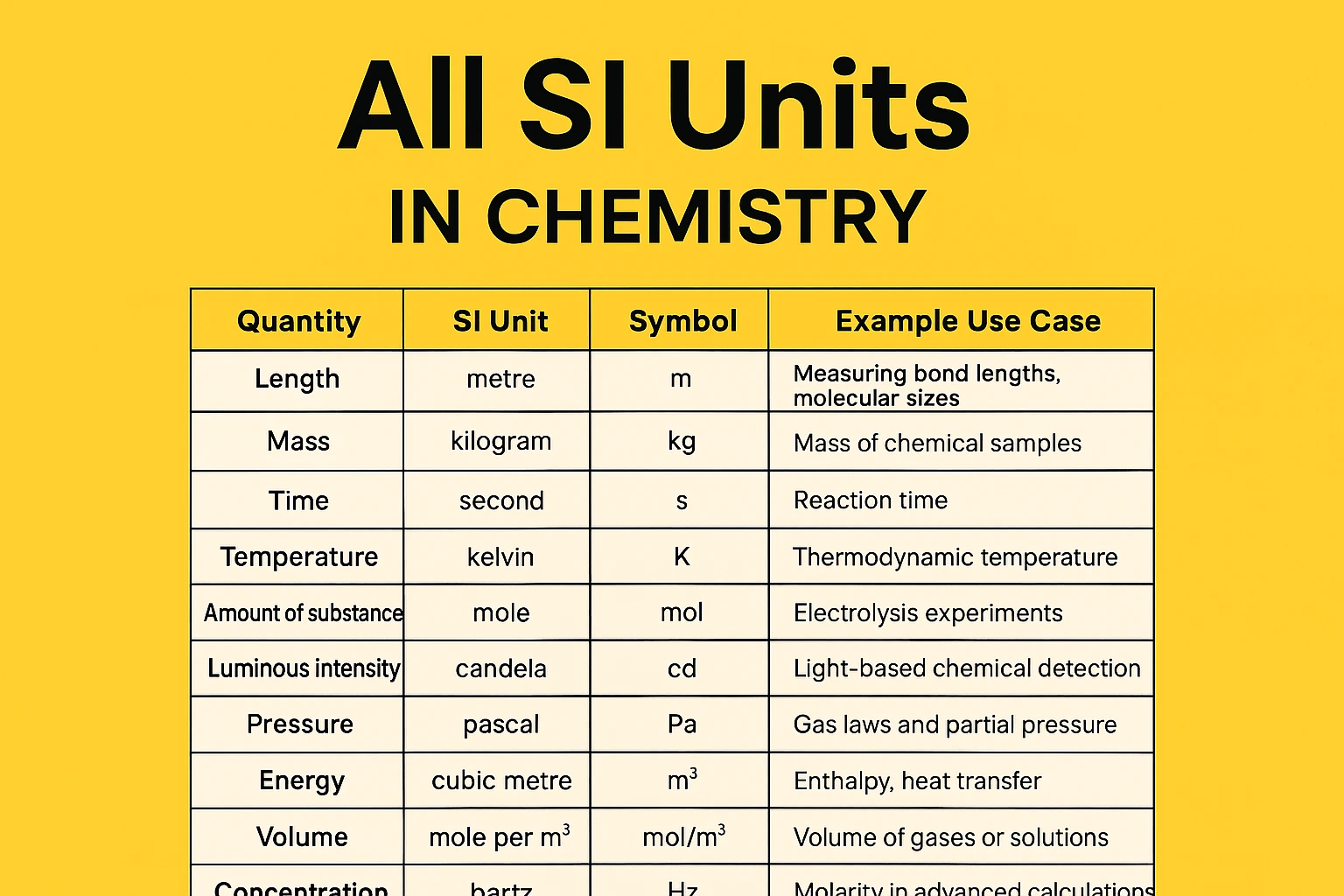
SI Units Table in Chemistry
| Physical Quantity | SI Unit Name | SI Unit Symbol | Explanation / Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m | Bond lengths, distances between atoms |
| Mass | kilogram | kg | Mass of substances in reactions |
| Time | second | s | Reaction time, half-life |
| Temperature | kelvin | K | Thermodynamic temperature |
| Amount of substance | mole | mol | Number of atoms/molecules using Avogadro’s number |
| Electric current | ampere | A | Current in electrochemical cells |
| Luminous intensity | candela | cd | Rare in chemistry, light-based detection |
| Volume | cubic metre | m³ | Volume of gas or solution |
| Density | kilogram per cubic metre | kg/m³ | Mass per unit volume of a substance |
| Concentration | mole per cubic metre | mol/m³ | Molar concentration |
| Energy | joule | J | Heat, enthalpy, work |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa | Gas pressure, partial pressures |
| Force | newton | N | Forces in molecular structures |
| Frequency | hertz | Hz | Vibrational frequency (e.g., in spectroscopy) |
| Power | watt | W | Rate of energy transfer |
| Electric charge | coulomb | C | Charge transferred in electrolysis |
| Voltage (potential diff.) | volt | V | Potential across electrochemical cells |
| Capacitance | farad | F | Used in some electrochemical studies |
| Resistance | ohm | Ω | Resistance in circuits |
| Conductance | siemens | S | Inverse of resistance |
| Catalytic activity | katal | kat | Rate of enzymatic or catalytic activity |
People Also Ask (FAQs)
1. What is the SI unit of amount of substance?
The SI unit for the amount of substance is the mole (mol). One mole equals (6.022 \times 10^{23}) particles — known as Avogadro’s number.
2. Why are SI units important in chemistry?
SI units create consistency. They help scientists across the world share, reproduce, and verify chemical data and experiments without confusion.
3. What is the SI unit of temperature in chemistry?
The SI unit of temperature is kelvin (K). It’s used in thermodynamic calculations, unlike Celsius or Fahrenheit.
4. What is the SI unit of concentration?
It is moles per cubic meter (mol/m³). In practice, moles per liter (mol/L) is often used for convenience.
5. Is liter an SI unit?
No. Liter (L) is a non-SI unit but widely used. The official SI unit for volume is cubic meter (m³).
Learn Chemistry Smarter — Download Study Friend
Want to master more than just SI units? 🔬
Study Friend gives you:
- AI-generated flashcards, mind maps, and summaries
- Bite-sized chemistry facts and formulas
- Smart search for any topic — anywhere, anytime
- Global syllabus coverage — perfect for high school & college students
🎓 Join thousands of learners worldwide who are learning faster and scoring better.
👉 Download Study Friend App — Start learning chemistry the smart way.