All SI Units Table in Physics (With Examples)
The International System of Units (in short, SI Units) is the modern form of the metric system. It’s used worldwide in Science, engineering, and everyday measurements. This topic is important for students in high school and college. It covers the fundamental of physics and provides a basic understanding of the physical world. In today’s post, we’ll go through the SI units table in physics with real-life examples.
📚 Want to quickly revise SI units, physics formulas, or generate flashcards on the go? Try Study Friend – your AI-powered study app for instant learning tools, concept explainers, mindmaps, and more.
SI Units Table in Physics (With Examples)
📏 Fundamental SI Units
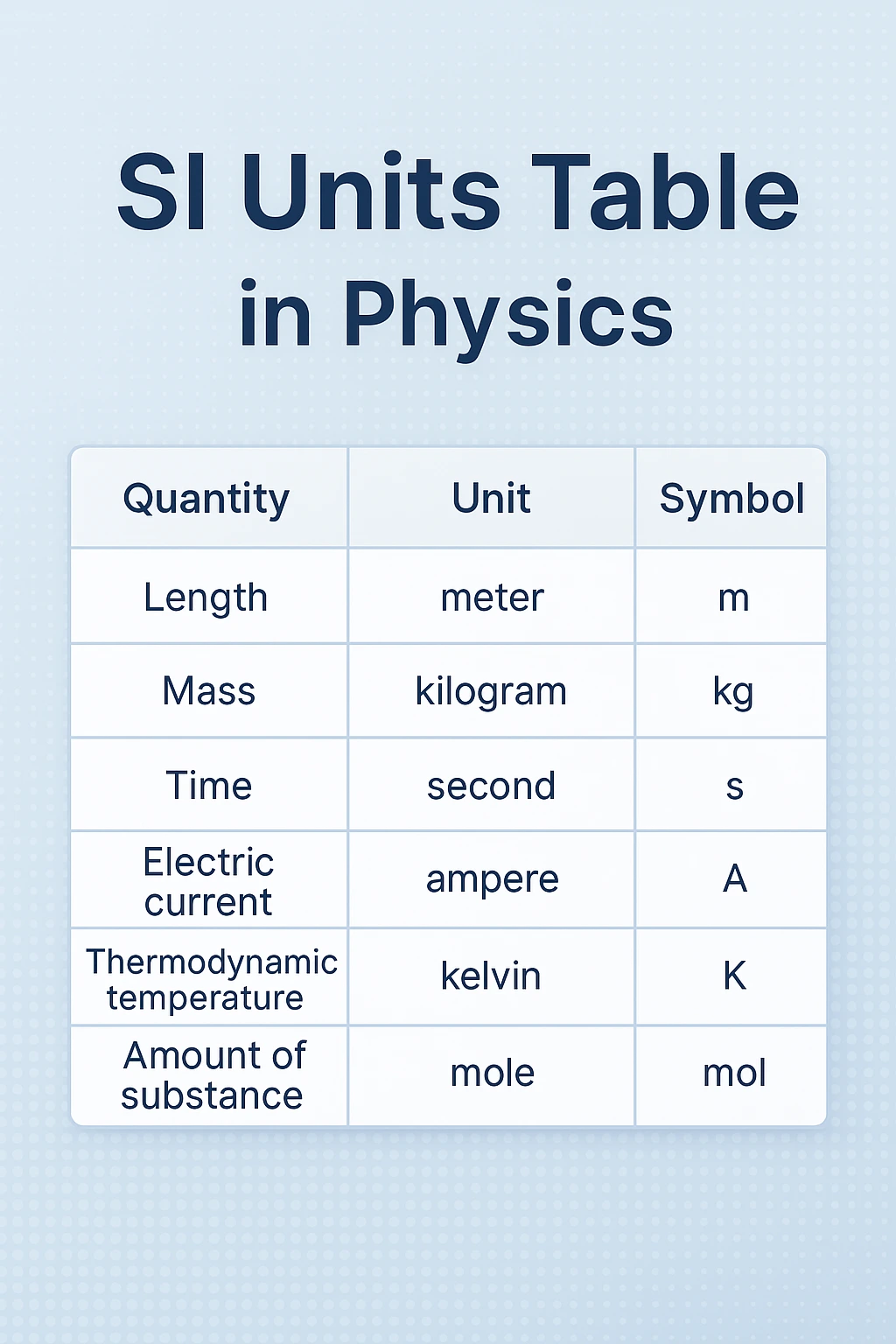
| Quantity | SI Unit Name | Symbol | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m | Distance between two cities |
| Mass | kilogram | kg | Weight of a bag of rice |
| Time | second | s | Time taken to boil water |
| Electric Current | ampere | A | Current in household wiring |
| Temperature | kelvin | K | Room temperature ≈ 293 K |
| Amount of Substance | mole | mol | One mole of water = 6.022 × 10^23 molecules |
| Luminous Intensity | candela | cd | Brightness of a candle |
⚙️ Derived SI Units in Physics
| Quantity | Unit Name | Symbol | Expressed As | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | square metre | m² | m × m | Size of a classroom |
| Volume | cubic metre | m³ | m × m × m | Volume of a fridge |
| Speed / Velocity | metre per second | m/s | m ÷ s | Car speed (e.g., 20 m/s) |
| Acceleration | metre per second² | m/s² | m ÷ s² | Gravity ≈ 9.8 m/s² |
| Force | newton | N | kg·m/s² | Force to lift an object |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa | N/m² | Air pressure ≈ 101325 Pa |
| Energy / Work / Heat | joule | J | N·m | Heat energy in a calorie ≈ 4.184 J |
| Power | watt | W | J/s | Lightbulb power (e.g., 60 W) |
| Electric Charge | coulomb | C | A·s | Battery charge |
| Electric Potential (Voltage) | volt | V | W/A | Voltage of AA battery ≈ 1.5 V |
| Electric Resistance | ohm | Ω | V/A | Resistance in an electric circuit |
| Electric Conductance | siemens | S | 1/Ω | Conductance of copper wires |
| Magnetic Flux | weber | Wb | V·s | Magnetic field through a coil |
| Magnetic Field Strength | tesla | T | Wb/m² | MRI machine field ≈ 1.5 T |
| Inductance | henry | H | Wb/A | Inductance in transformer coils |
| Luminous Flux | lumen | lm | cd·sr | Light output of LED bulb ≈ 800 lm |
| Illuminance | lux | lx | lm/m² | Office lighting ≈ 500 lx |
| Radioactivity | becquerel | Bq | decays/s | Radioactive decay rate |
| Absorbed Radiation Dose | gray | Gy | J/kg | Radiation therapy dose |
| Equivalent Radiation Dose | sievert | Sv | J/kg | Radiation safety limit ≈ 0.05 Sv/year |
🧠 Summary
- The 7 fundamental SI units form the base of all physical measurements.
- Derived units are combinations of these, used to describe more complex phenomena like force, energy, and power.
- SI units provide a universal language for physics, ensuring consistency and precision in global communication.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the SI unit of force?
Newton (N) – It is the force required to accelerate 1 kg of mass by 1 m/s².
What is the SI unit of energy?
Joule (J) – It is the work done when a force of 1 newton moves an object 1 meter.
What is the SI unit of power?
Watt (W) – It is the rate of doing work or transferring energy at 1 joule per second.
What is the SI unit of electric current?
Ampere (A) – It measures the amount of electric charge passing a point per second.
What is the SI unit of temperature?
Kelvin (K) – It is the base unit of temperature used in scientific measurements.
What is the SI unit of pressure?
Pascal (Pa) – It equals one newton per square meter (N/m²).
What is the SI unit of luminous intensity?
Candela (cd) – It measures the brightness of a light source in a particular direction.
What is the SI unit of magnetic field?
Tesla (T) – It is equal to one weber per square meter.
What is the SI unit of charge?
Coulomb (C) – It represents the quantity of electric charge.
What is the SI unit of frequency?
Hertz (Hz) – It measures the number of occurrences of a repeating event per second.
Want to quickly revise SI units, formulas, or create flashcards and mind maps?
👉 Try Study Friend – your AI-powered study app for smarter, faster learning.
Want more physics cheat sheets like this? Bookmark this site. Stay curious and keep exploring the universe!